| Sonoran Desert |
|
|
This section is the hot part of the Basin and Range Province, from the eastern end of the Transverse Ranges and the Salton Trough east to Arizona. Some rain falls during the summer. The section is in MLRA 30.
Geomorphology. Widely separated short ranges in desert plains. Basin and Range geomorphic province.
Lithology. Cenozoic sedimentary rocks and alluvial eolian deposits, and Precambrian to Cenozoic granitic and metamorphic rocks.
Soil Taxa. Aridisols and Entisols in combination with thermic or hyperthermic soil temperature regimes and aridic soil moisture regimes.
Vegetation. Predominant potential natural communities includes the Creosote bush series, Creosote bush - white bursage series, Mixed salt bush series, Blue palo verde - ironwood - smoke tree series, Mesquite series, Ocotillo series and Foothill paloverde - saguaro series.
The following series are found throughout the section and are not restricted to or extensive in any subsection. Series dominated by exotic plants are not listed under subsections unless they are extensive and stable.
Series dominated by exotic plants: Gaint reed series and Tamarisk series.
Series that can occur in all subsections, but are not extensive: Bulrush series, Bulrush - cattail series, Cattail series, Duckweed series, Mosquito fern series, Pondweeds with floating leaves series, Pondweeds with submerged leaves series, Saltgrass series, Sedge series and Spikerush series.
Series restricted to riparian settings: Arrow weed series, Black willow series, Fremont cottonwood series, Mixed willow series, Mulefat series, Narrowleaf willow series and Red willow series.
Fauna. Reserved.
Elevation. 250 to 4400 feet.
Precipitation. 3 to 6 inches. Occurs as winter rain and high intensity summer thunderstorms.
Temperature. 60░ to 75░F.
Growing Season. 250 to 325 days.
Surface Water Characteristics. Mostly bedrock controlled channels in mountains that carry seasonal flows to alluvial channels below. Channels terminate in basins or the Colorado River.
Disturbance Regimes.
Climate: Flash floods are commonly associated with summer precipitation events.
Land Use. Composition and successional sequence of some communities has changed because of plant and animal species introduced between the late 1800Æs and early 1900Æs related to mining, agriculture and grazing. Since the early 1900Æs, significant effects on some plant and animal species occur at widely scattered locations associated with military installations, agriculture, recreational activities and expanding settlement.
Cultural Ecology. Humans have been utilizing the area for some 10,000 years, with early Paleoindian hunting assemblages documented at sites in the Mojave. After the end of the Pleistocene, Archaic assemblages reflect extensive practice of seasonal rounds for diversified hunting and gathering. Agricultural practices of Colorado River cultures spread through scattered areas during Late Prehistoric times, after A.D. 1000. Contemporary attitudes and beliefs are varied; lifestyle is rural. The economy emphasizes government employment, mining, ranching, and recreation.
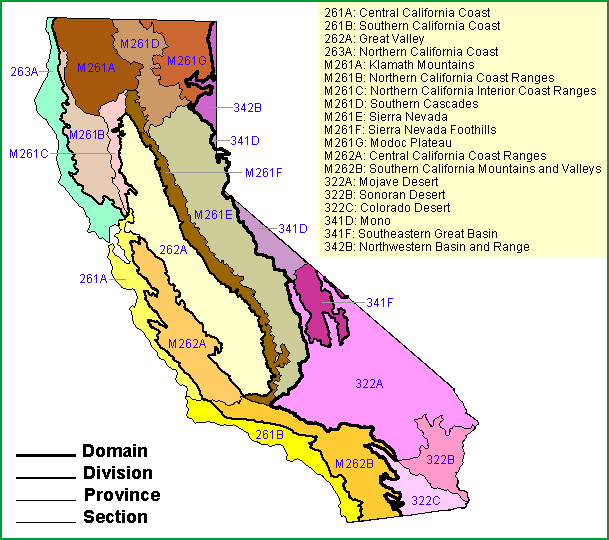
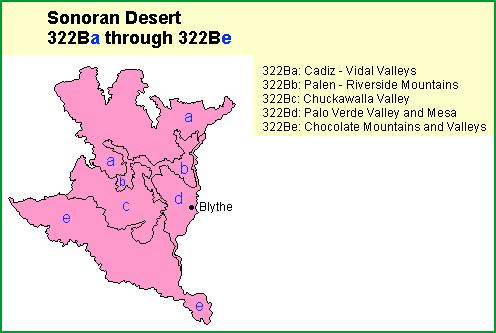
Subsections. The Sonoran Desert section is divided into 5 subsections
Map
Cadiz - Vidal Valleys -Palen - Riverside Mountains
Chuckawalla Valley - Palo Verde Valley and Mesa- Chocolate Mountains and Valleys