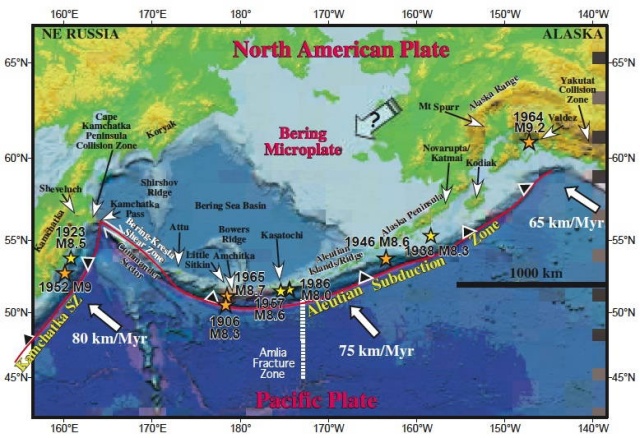
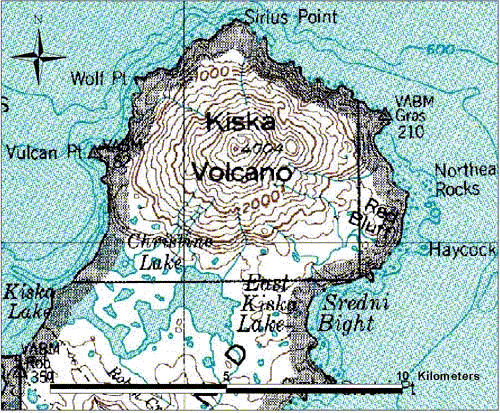
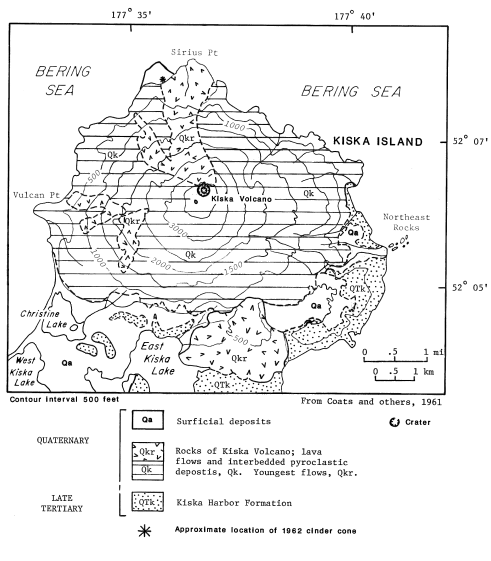
| Rat Islands. Kiska Island |
|
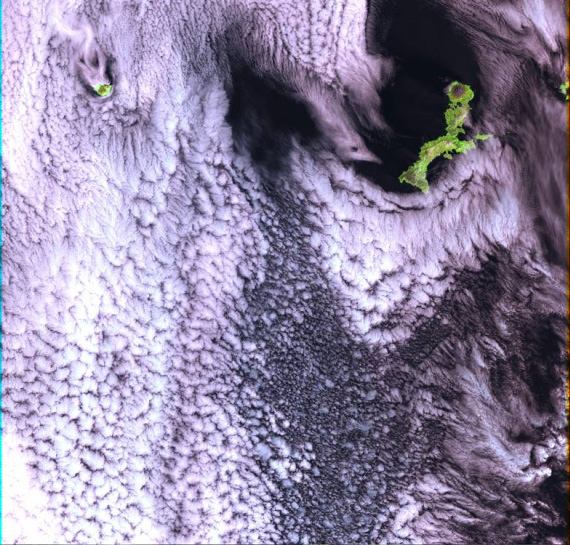
Landsat 7 ETM+ image, with Kiska Volcano on the right-hand island and Buldir on the left |
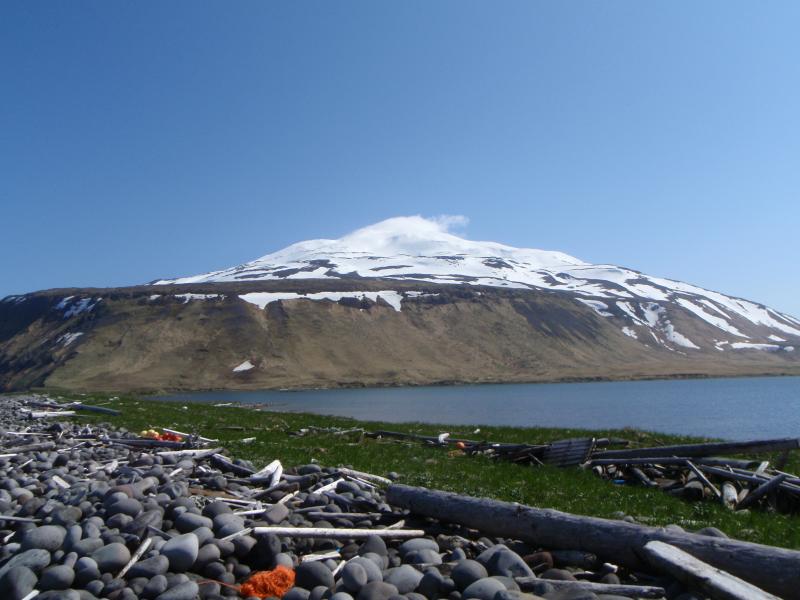
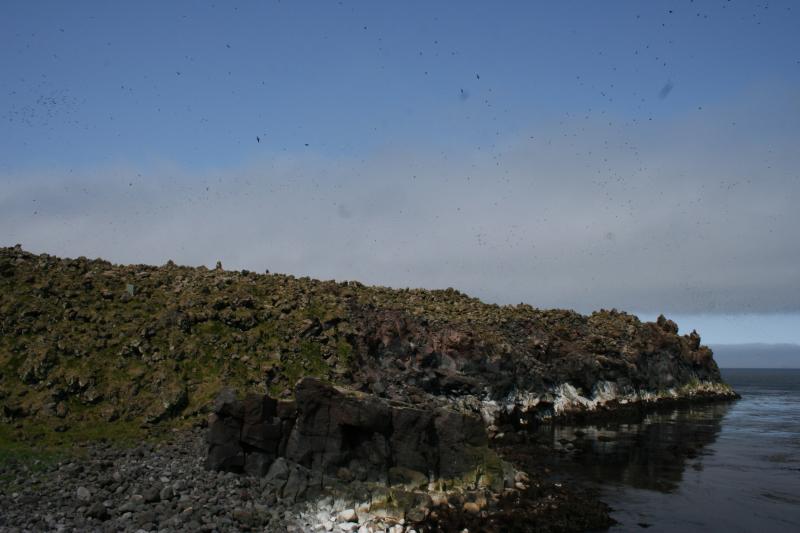
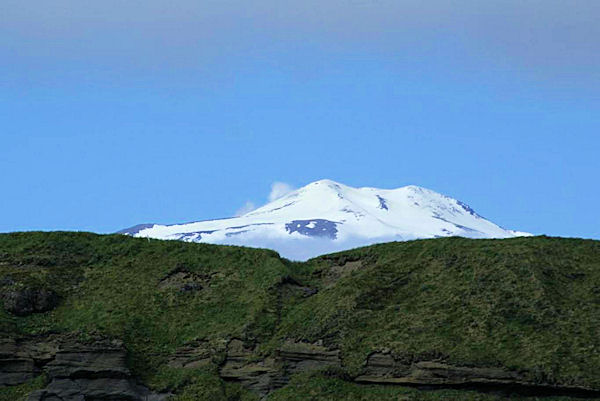
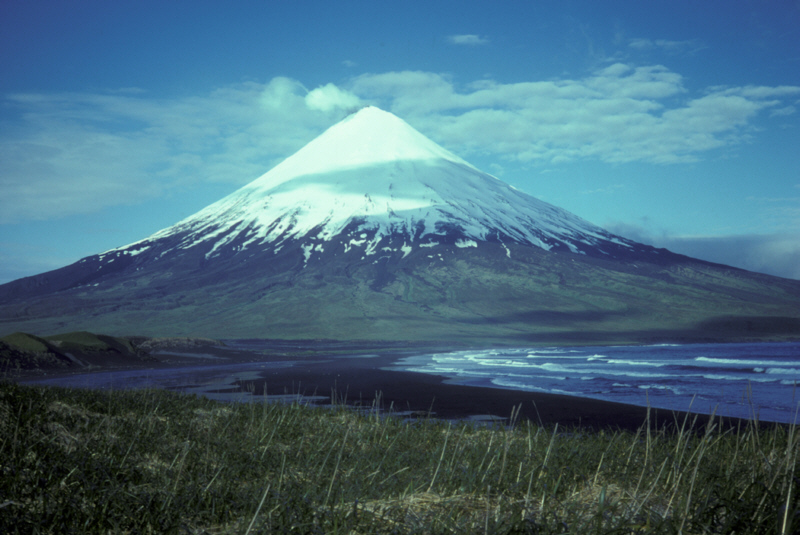
Kiska volcano. Kiska Volcano is a stratovolcano, 8.5 by 6.4 km in diameter at its base and 1,221 m high, located on the northern end of Kiska Island.On January 24, 1962, an explosive eruption occurred, accompanied by lava extrusion and the construction of a cinder cone about 30 m high at Sirius Point on the north flank of Kiska Volcano, 3.1 km from the summit of the main cone (Anchorage Daily News, January 30, 1962). A second eruption that produced a lava flow was reported to have occurred on March 18, 1964 (Bulletin of Volcanic Eruptions, 1964).Since then the volcano has emitted steam and ash plumes as well as smaller lava flows. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kiska |
Kiska. This image is found in Miller, T. P., McGimsey, R. G., Richter, D. H., Riehle, J. R., Nye, C. J., Yount, M. E., and Dumoulin, J. A., 1998, Catalog of the historically active volcanoes of Alaska: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report OF 98-0582, 104 p.,http://www.avo.alaska.edu/images/image.php?id=539 |
Kiska summit elevation 1220 m , stratovolcano Kiska volcano is located in the Rat Island group, Aleutian Islands, Alaska. Kiska is the westernmost island in the Rat group. The island was sighted by Bering during a voyage in 1741, when it was occupied by an Aleut population.Kiska contains one of the best harbours in the Aleutian Islands. The coastline of Kiska volcano is continuous cliff that ranges in height from tens of metres to over 500 m.Kiska is a young composite andesite volcano, occupying the northern part of the island. The southern side of the island is an extension of a submarine ridge.Kiska volcano and harbour contain interbedded andesitic to basaltic pyroclastic rocks, lava flows, and sedimentary rocks formed from volcanic debris. The eastern side of the island was modified by glaciers. A thin layer of volcanic ash on the island has been erupted from nearby volcanoes.A region of hummocky seafloor terrain extends 30 km NNW of Kiska volcano. This indicates a previous edifice failure at the volcano, even though no subaerial evidence exists.1990 Eruption Ash emissions were observed at Kiska volcano on 1st June 1990. Emission came from an upper flank vent. 1987 eruption An eruption plume extending 60 km east of Kiska volcano was detected on satellite images on 15th April 1987.1969 Eruption On 11th September 1969 an eruption was observed, with ash to 400 m high and steam to 4000 m. 1962 Eruption An eruption in 1962 formed a 30 m high cinder cone.Possible eruption in 1943 Newspaper reports in June 1943, shortly before the island was occupied by American and Canadian forces, describe an ash eruption accompanied by earthquakes. When the mountain was climbed in 1947, there was no evidence of recent ash emission, and no solfataric or fumarolic activity.1905 SolfataraActive solfatara were observed in the crater in 1905.Kiska Volcano Eruptions 1990, 1987, 1969, 1964, 1962, 1927?, 1907? http://www.volcanolive.com/kiska.html |
From Miller and others (1998): "Kiska Volcano is a stratovolcano, 8.5 by 6.4 km in diameter at its base and 1221 m high, on the northern end of Kiska Island. A slightly elliptical crater, about 0.4 km in diameter and breached on the north, occupies the summit. A parasitic 30-m-high cinder cone, formed in 1962 near sea level, occurs at Sirius Point and an older parasitic cone, now leveled by marine erosion, occurs at sea level 5.6 km southwest of Kiska Volcano. "The southern part of Kiska Island has been glacially eroded, but the volcano shows no evidence of glacial dissection (Coats, 1956). Surface lava flows are thus younger than the last major glaciation. Five of the youngest lava flows (unit Qkr) have been mapped separately by Coats and others (1961) based on geomorphic expression; the flows of block lava have steep fronts as much as 30 m high. Source areas of the flows range from the base of the cone to the summit. The highest flows appear to have emerged from the summit crater through the breached north wall. "Kiska Volcano is underlain and flanked on the south by the remains of an older composite volcano; a single K-Ar age of 5.5 +/- 0.7 m.y. is cited in Marlow and others (1973) for an andesitic lava flow in this older volc http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcinfo.php?volcname=Kiska |
looking north (from Kavalga) |
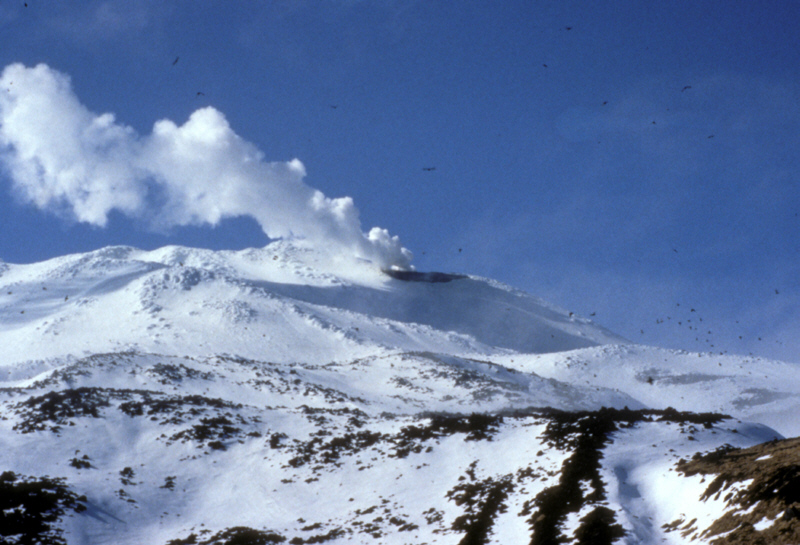
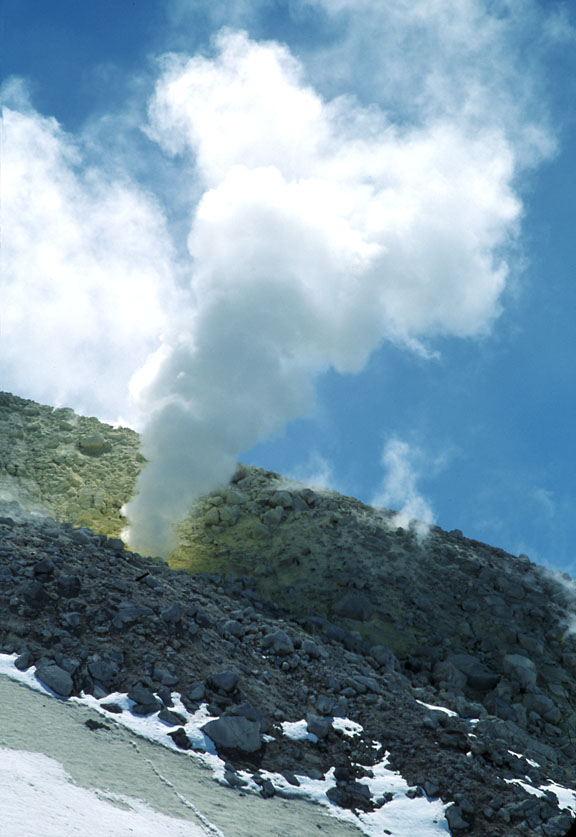
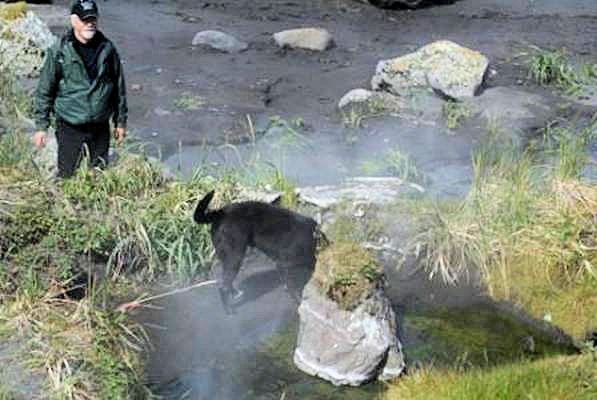
Fumarolic activity at Kiska Volcano http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
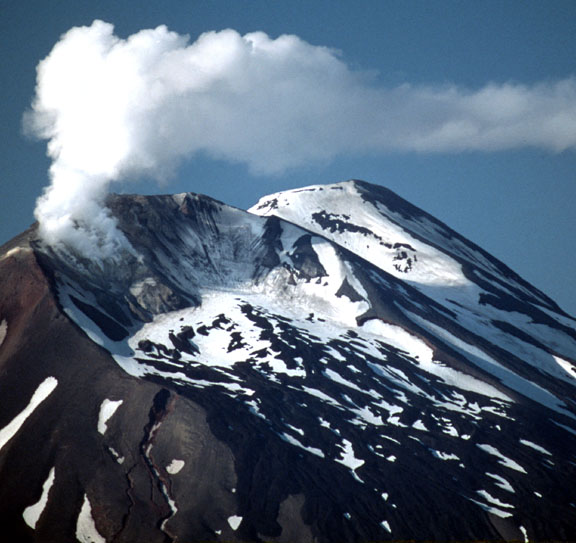
Kiska Volcano, looking west from the eastern dome. Image courtesy of Ian L. Jones, Department of Biology, Memorial University http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
Auklets on Kiska, with fumarole field visible in upper right, courtesy of Alex Bond Photograph courtesy of Alex Bond - http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
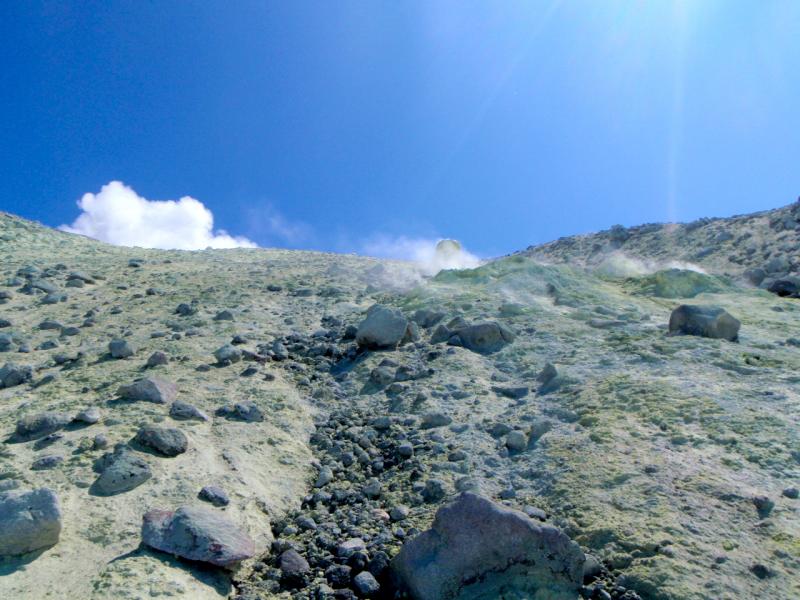
Active fumarole field on Kiska, photograph courtesy of Alex Bond http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
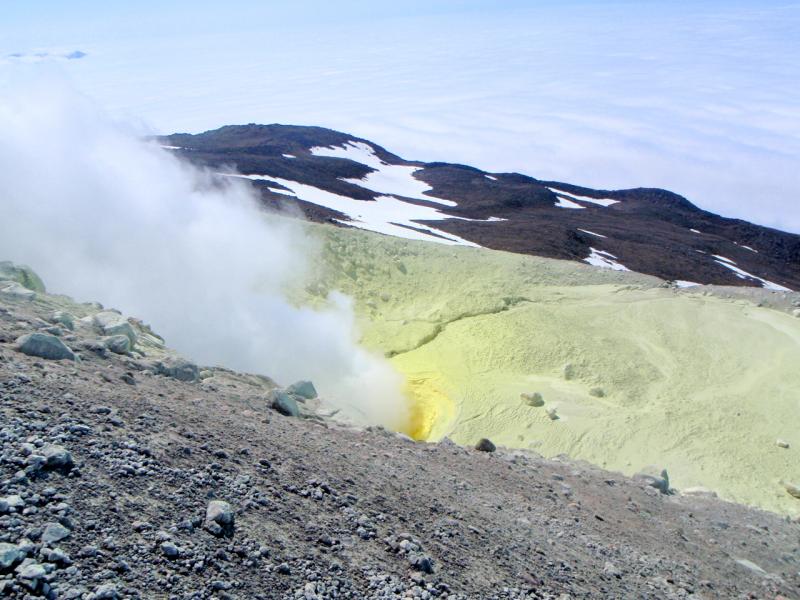
Active fumarole on Kiska - the yellow coloring is sulfur. Photograph courtesy of Alex Bond - http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
Kiska Volcano, steaming northern vent. Image courtesy of Ian L. Jones, Department of Biology, Memorial University http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
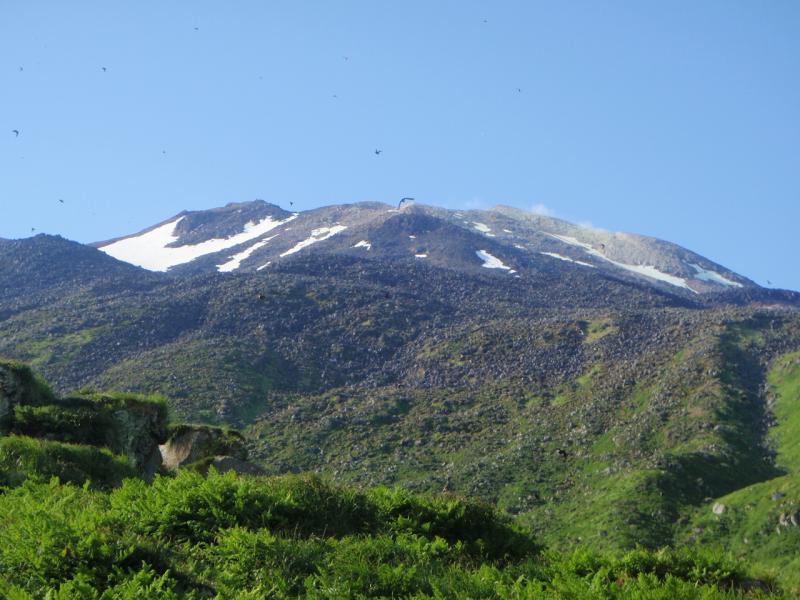
Image of Kiska volcano, taken during summer 2008 field work by Alex Bond from Memorial University''s Department of Biology http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
Image of Kiska volcano, taken during summer 2008 field work by Alex Bond from Memorial University''s Department of Biology http://www.avo.alaska.edu/volcanoes/volcimage.php?volcname=Kiska |
Kiska Volcano |
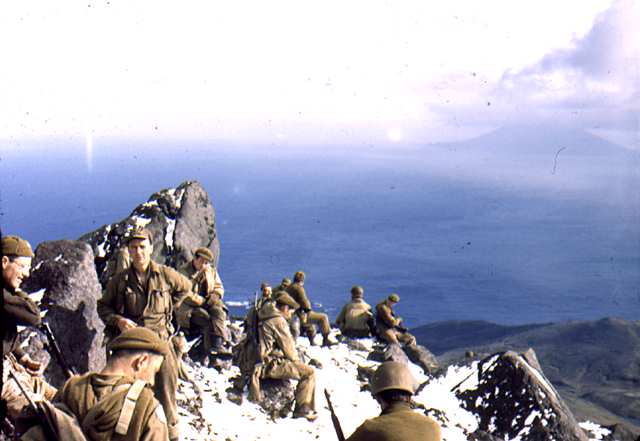
Soldiers on top of Kiska Volcano,http://aam.govst.edu/projects/nhayes/primarysourcesvolcanoes.htm |
Kiska |
Clevelend |
Kanaga Volcano. 1300 m, is a spectacular symmetrical cone situated on the northern tip of Kanaga Island. It is a youthful volcano formed within an older caldera, whose remnants can be seen as the crescent-shaped Kanaton Ridge just to the south of the cone. The most recent eruptions in the mid-1990s sent lava flows from the summit crater all the way down into the sea on the north side of the volcano. Since Kanaga is located just 15 miles (25 km) west of the "major" city of Adak, access should be somewhat easier than for many other locations in the outer Aleutians |
Tanaga Hot Spring bay |
Tanaga |
Tanaga |
Sugarloaf Peak from the east |
amagat island http://www.summitpost.org/amagat-island/737705 |
Amagat Island -http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_islands_of_Alaska |
http://www.summitpost.org/amagat-island/737705 amagat ialand nature volcano
http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&bav=on.2,or.r_gc.r_pw.,cf.osb&biw=1024&bih=587&wrapid=tlif133947476972511&um=1&ie=UTF-8&tbm=isch&source=og&sa=N&tab=wi&ei=UcPWT54hxcvZBdLm5L4P&q=Amagat%20Island
http://www.melindawebster.com/aleutians2/ pictures